Ancient Egypt, with its rich history and vibrant culture, had a complex religious system. At the heart of this system were the deities, worshipped and venerated for thousands of years. This article provides an overview of some of the most significant Egyptian gods, understanding that the entire pantheon comprises a multitude of deities, each with its significance and mythological background.
Creation and Primordial Deities
Atum (or Atem)
- Role: Often considered the creator god.
- Association: Sun and creation.
- Symbolism: Often depicted as a man wearing either the royal headcloth or the dual white and red crown of Upper Egypt and Lower Egypt, respectively.

Nun
- Role: Embodies the primordial waters.
- Association: Chaos and waters of creation.
- Symbolism: Rarely personified but essential in Egyptian creation myths.
Celestial Deities
Nut (or Nuit)
- Role: Sky goddess.
- Association: The heavens, the barrier separating the forces of chaos from the ordered cosmos in the world.
- Symbolism: Often portrayed as a woman arched over the earth god Geb, her body covered in stars. Nut is usually shown in a protective posture, representing her role as the sky itself, offering a shield over the world.
In Egyptian mythology, Nut was the sister and wife of Geb, the earth god, and the mother of Osiris, Isis, Set, and Nephthys. She was considered a friend to the dead since the sky goddess was a symbolic mother to the pharaohs, who were described as stars within her body, which would rise in the eastern sky at night after their death.

Major Deities
Ra (or Re)
- Role: Sun god.
- Association: Creator, ruler of the pharaohs.
- Symbolism: Often portrayed with the head of a hawk crowned with a sun disc encircled by a serpent.

Osiris
- Role: God of the afterlife, death, and resurrection.
- Association: Regeneration, judge of the dead.
- Symbolism: Typically shown as a mummified king holding a crook and flail.

Isis
- Role: Mother goddess.
- Association: Magic, motherhood, and protection.
- Symbolism: Often depicted with a throne-shaped crown or with wings spread protectively.

Horus
- Role: Sky god, protector of the pharaoh.
- Association: Kingship.
- Symbolism: Often shown as a falcon or as a man with the head of a falcon.

Set (or Seth)
- Role: God of chaos, disorder, and storms.
- Association: Desert, infertility.
- Symbolism: Depicted with an unidentified animal head, referred to as the ‘Set animal’.
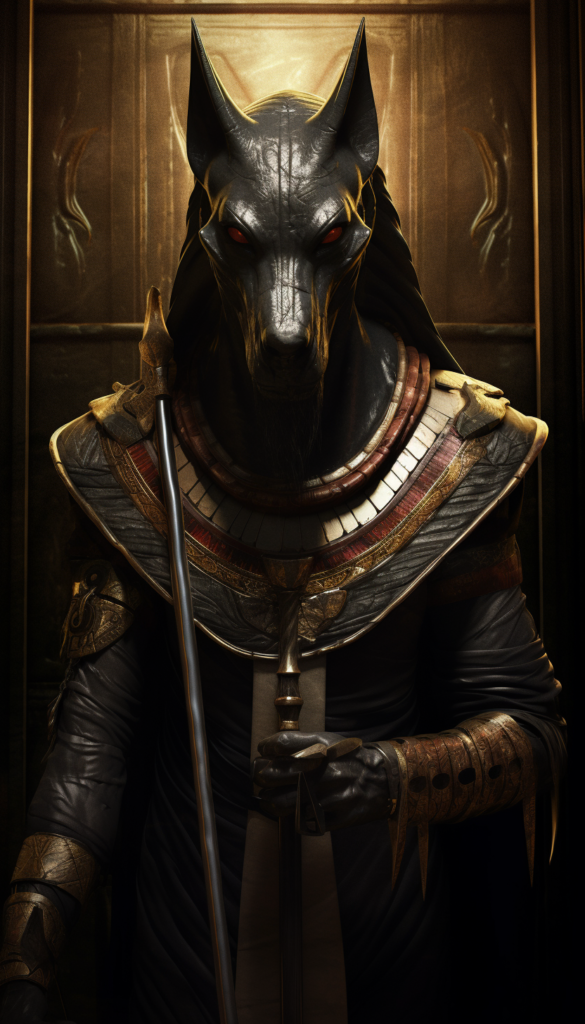
Anubis
- Role: God of mummification.
- Association: Afterlife and burial ceremonies.
- Symbolism: Often portrayed as a man with the head of a jackal.

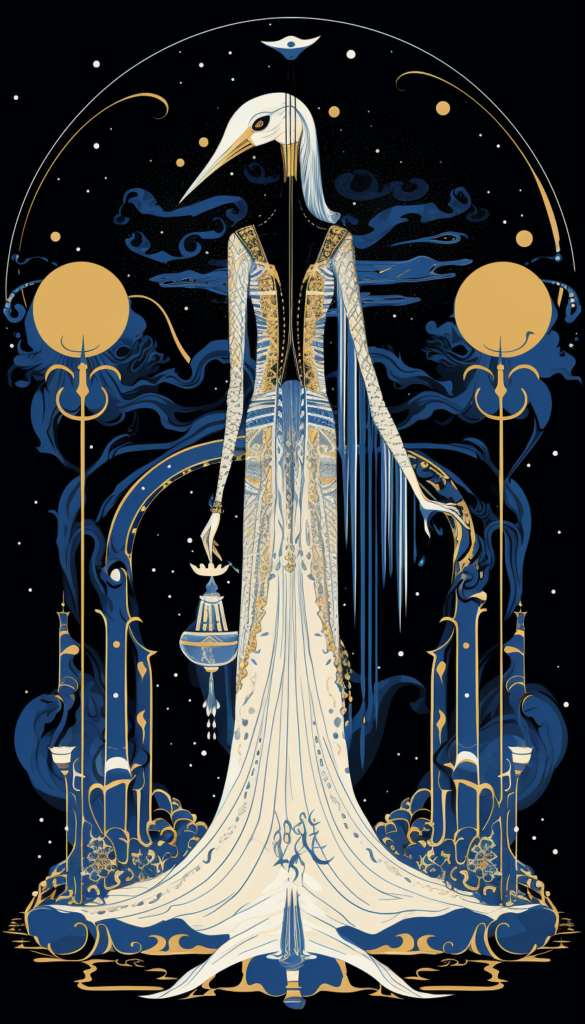
Thoth
- Role: God of writing, knowledge, and wisdom.
- Association: Arbitrator of divine disputes, magic, and the arts.
- Symbolism: Commonly shown as a man with the head of an ibis, sometimes a baboon.

Protection and Nature Deities
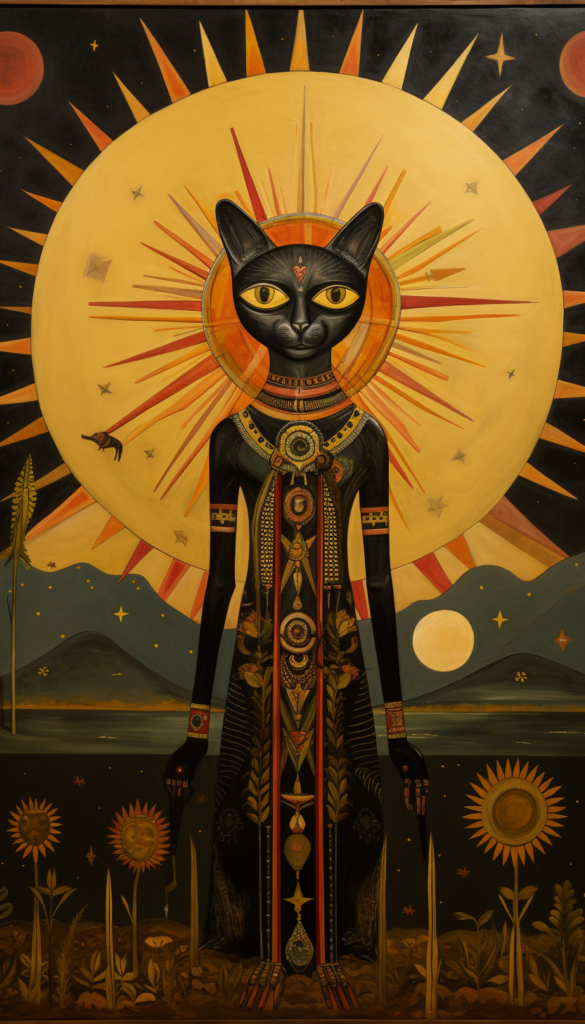
Bastet – Role: Goddess of home, fertility, and protector of pharaohs. – Association: Cats, joy, and dance. – Symbolism: Often depicted as a lioness or a woman with the head of a lioness.

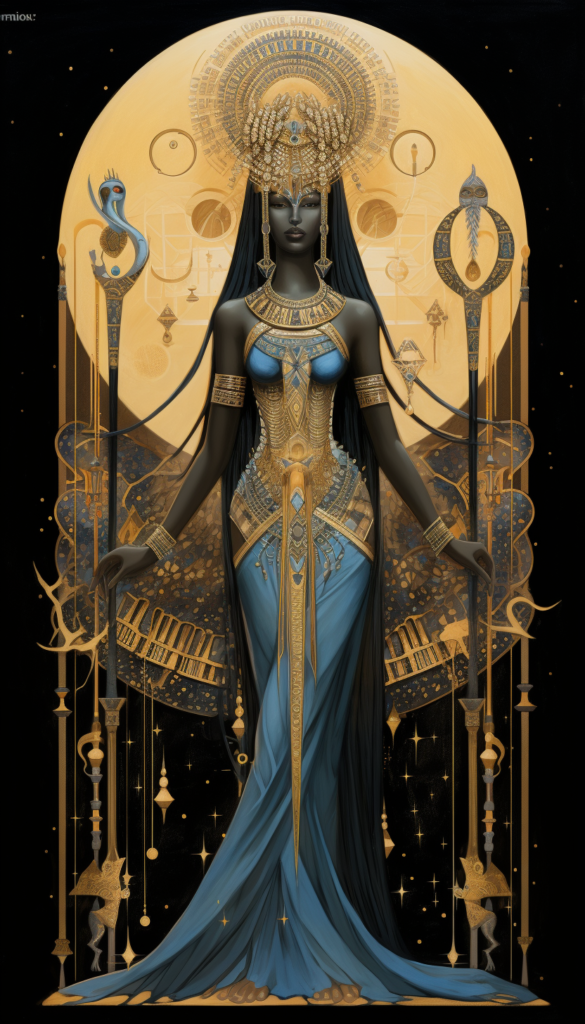
Hathor – Role: Goddess of music, love, and dance. – Association: Sky, sun, and fertility. – Symbolism: Commonly portrayed as a woman with the head of a cow or having cow’s ears.

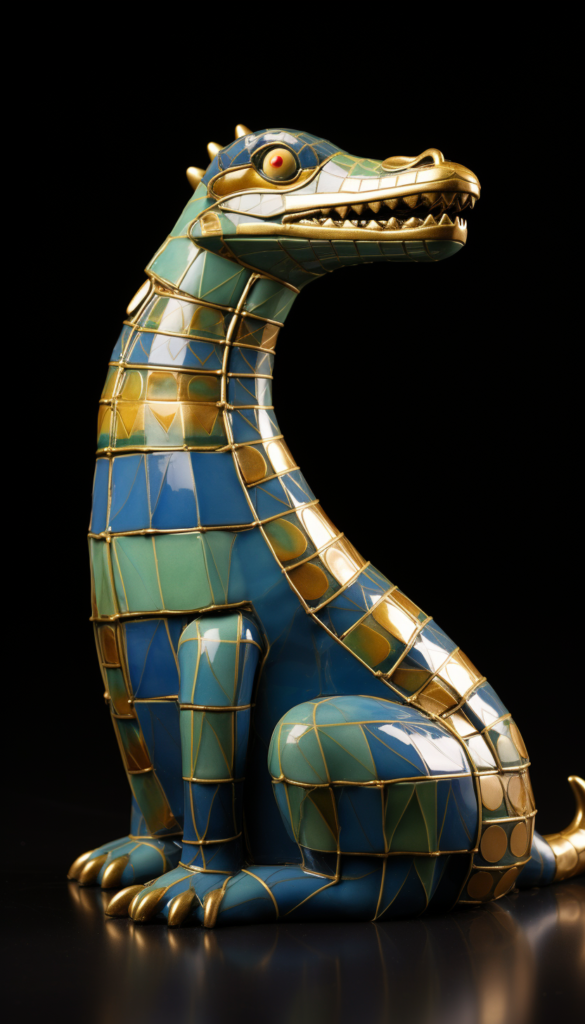
Sobek – Role: God of the Nile, military, and fertility. – Association: Crocodiles. – Symbolism: Shown as a man with a crocodile head.

Maat – Role: Goddess of truth, balance, and order. – Association: Cosmic order, justice. – Symbolism: Portrayed as a woman with an ostrich feather on her head.

…
Chart of the Egyptian Pantheon:
| God/Goddess | Domain | Symbolism |
|---|---|---|
| Amun | Creator god, king of the gods | The sun disk, the ram |
| Amunet | Female counterpart of Amun | The serpent, the wind |
| Apep | The serpent of chaos | The night sky, the underworld |
| Anubis | God of embalming and the dead | The jackal, the scales of justice |
| Bastet | Goddess of cats, protection, and childbirth | The cat, the moon |
| Geb | God of the earth | The bull, the sky |
| Hathor | Goddess of love, music, and dance | The cow, the sistrum |
| Horus | God of the sky, kingship, and war | The falcon, the sun disk |
| Isis | Goddess of magic, motherhood, and death | The throne, the crescent moon |
| Maat | Goddess of truth, justice, and balance | The feather, the scales of justice |
| Nephthys | Goddess of the night, the dead, and mourning | The vulture, the desert |
| Nut | Goddess of the sky | The cow, the stars |
| Osiris | God of the underworld, resurrection, and agriculture | The mummified king, the green earth |
| Ra | The sun god | The sun disk, the scarab beetle |
| Seth | God of chaos, the desert, and storms | The desert jackal, the hippopotamus |
| Thoth | God of knowledge, writing, and magic | The ibis, the moon |
Conclusion
The Egyptian pantheon, with its myriad deities, provides a comprehensive understanding of how the ancients viewed the world around them. From creation myths to the complexities of the afterlife, these gods and goddesses played crucial roles in the religious and daily lives of the Egyptians. It’s worth noting that this overview just scratches the surface. Each deity had its temples, ceremonies, myths, and dedicated priesthood. Delving deeper into each one unveils a rich tapestry of stories, rituals, and beliefs that have shaped not just ancient Egypt, but also the broader understanding of mythology and religion.

